Simple Spatial Scaling Rules behind Complex Cities
Although most of wealth and innovation have been the result of human interaction and cooperation, we are not yet able to quantitatively predict the spatial distributions of three main elements of cities: population, roads, and socioeconomic interactions. By a simple model mainly based on spatial attraction and matching growth mechanisms, we reveal that the spatial scaling rules of these three elements are in a consistent framework, which allows us to use any single observation to infer the others. All numerical and theoretical results are consistent with empirical data from ten representative cities. In addition, our model can also provide a general explanation of the origins of the universal super-/sub-linear aggregate scaling laws and accurately predict kilometre-level socioeconomic activity. Our work opens a new avenue for uncovering the evolution of cities in terms of the interplay among urban elements, and it has a broad range of applications.
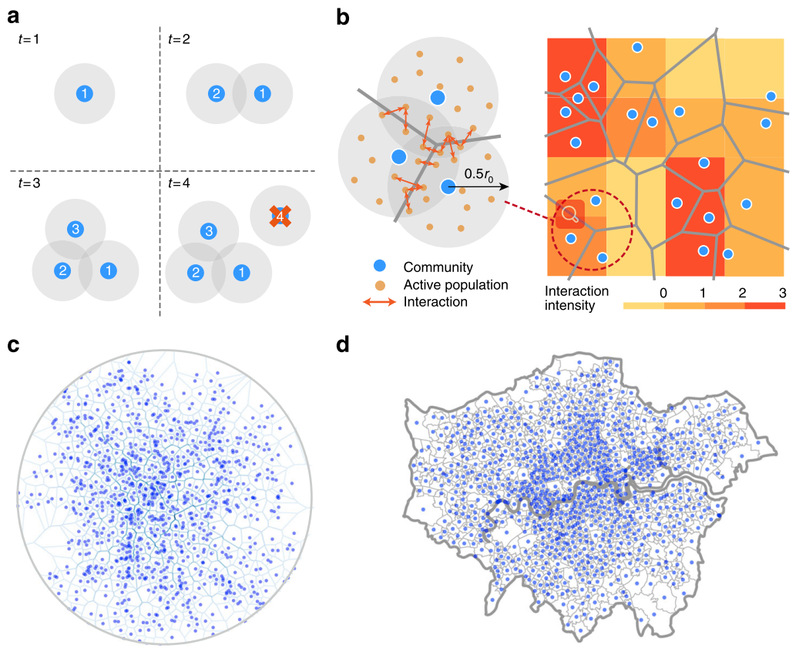

Spatial Scalings within Cities


Scaling Laws across Cities
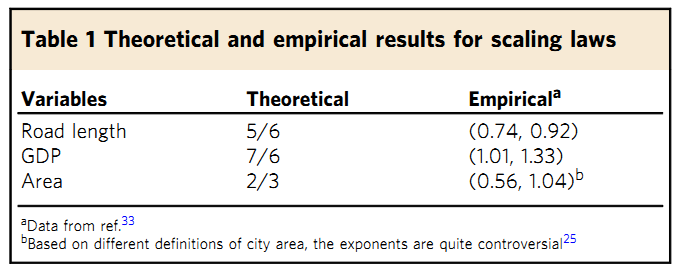
Active Population (AP)
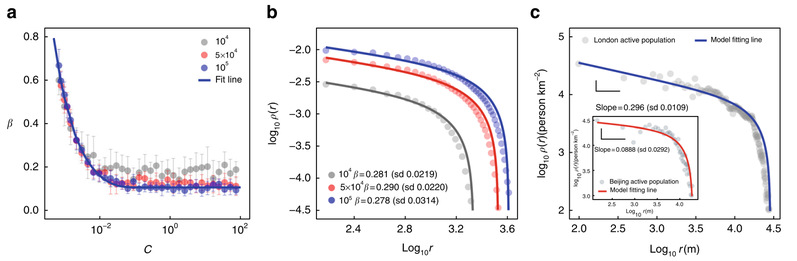
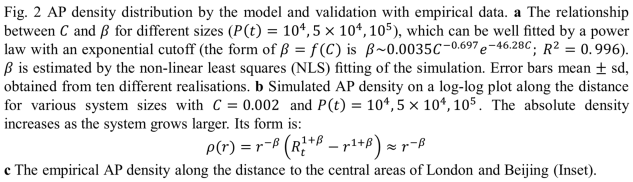
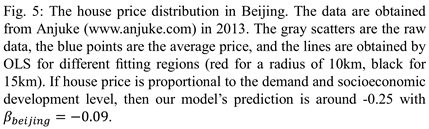
Predictions for House Price

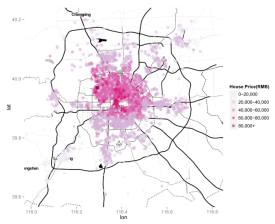
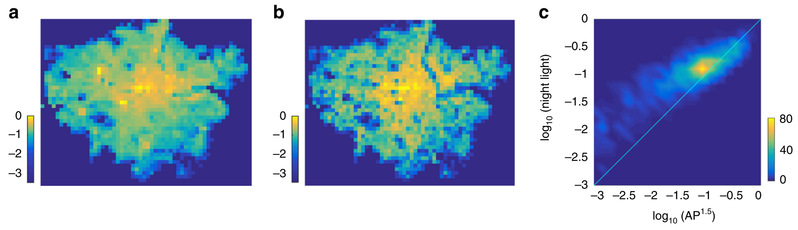
Quantifying Socio-economic Interactions
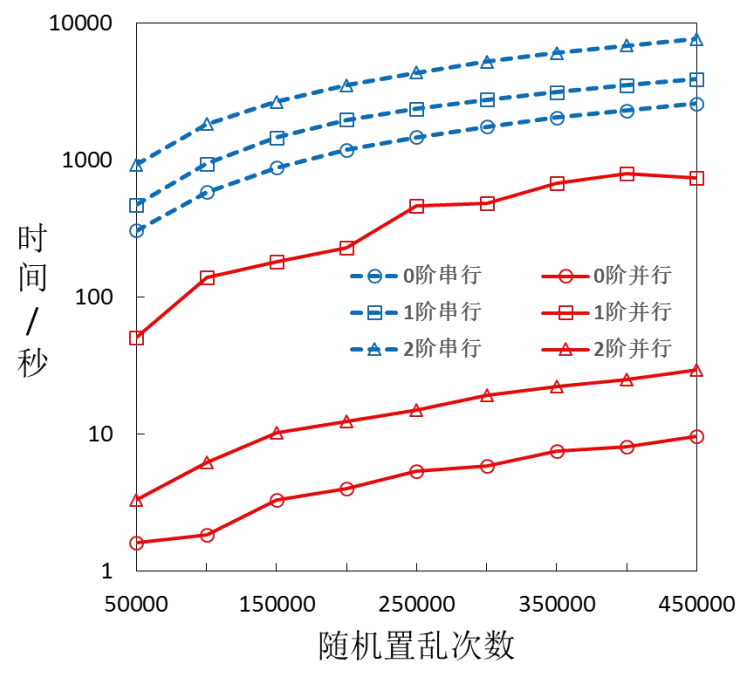
基于GPU的网络布局加速算法
Accelerated network layout algorithm on GPU
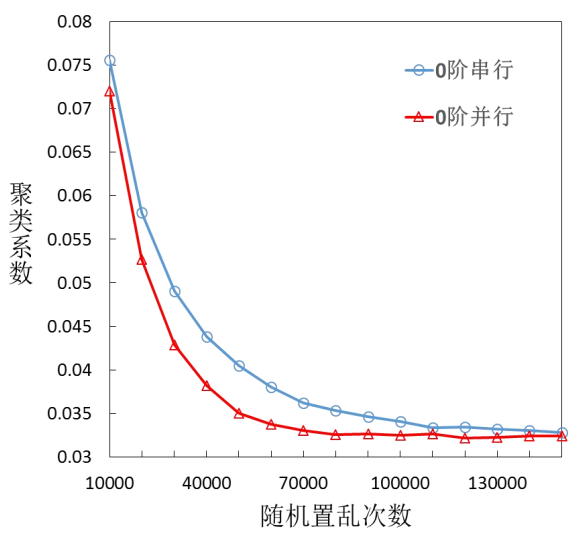
针对力导引网络布局算法中的斥力计算、引力计算和坐标更新,在GPU上实现了算法加速。

基于GPU的复杂网络零模型快速生成
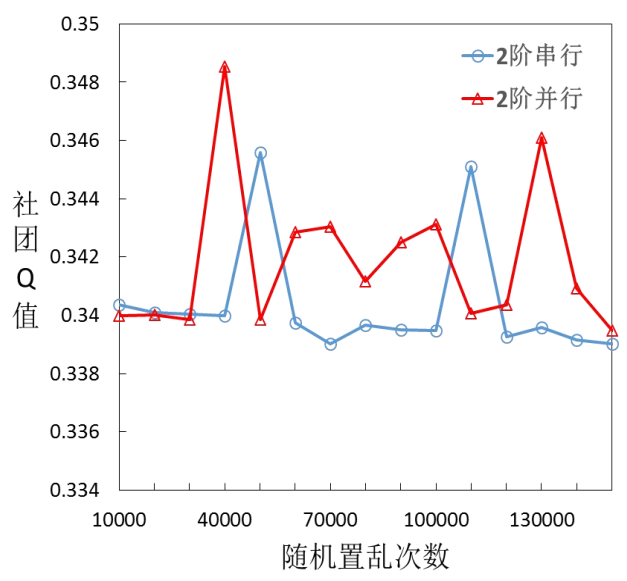
Generating null models for large networks on GPU


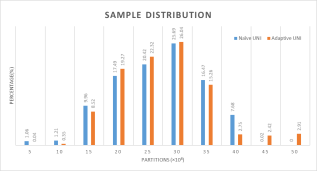
面向32位整数空间的微博用户ID自适应UNI采样
Adaptive UNI sampling user IDs of Weibo in 32-bit integer space
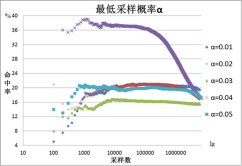
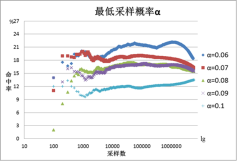
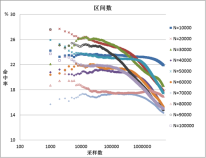
外国学者在对Facebook进行采样研究时,提出了一种基于接受-拒绝采样方法的无偏均匀采样法——UNI方法,并将其用作其它采样方法的评估基准值。然而他们同时也指出,UNI方法当时对于Facebook中为32位整数的用户ID是有效的,但Facebook将用户ID升级为64位整数后,该方法由于其极低的采样命中率而失效。为了研究64位整数空间甚至更大空间范围内的UNI采样方法,我们先提出了面向32位整数空间的自适应UNI采样方法,以提高UNI采样方法的采样命中率。
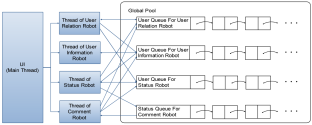
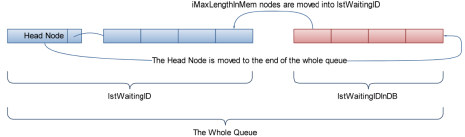
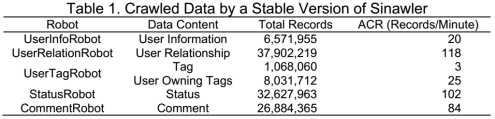
基于新浪微博API的多线程微博爬虫
SinawlerAdaptive UNI Sinawler: crawler for Weibo based on the open APIs